本筆記將會介紹我在 系統程式 所學到的東西。
Ch1 Background #
系統軟體(System software) #
系統程式的定義 #
是一種用來操作和控制電腦硬體的軟體,主要功能是作為使用者與硬體之間的橋樑,確保電腦能順暢運行。
以下都可以稱為系統軟體:
- Text editor
- compiler
- loader or linker
- debugger
- macro processors
- operating system
Machine dependency #
- 大部分系統軟體都具備機器依賴性(Machine dependency),需要在特定硬體架構上才能順利執行。
- 有些系統軟體並不會直接依賴計算機系統。
Simplified Instructional Computer (SIC) #
- 是一種假想的電腦,用來解釋計算機結構
- 分為以下兩個版本:
- Standard version (SIC)
- Extension version (SIC/XE)
向上兼容(upward compatible):SIC/XE 支援 SIC 全部的指令,但 SIC 不一定可以支援 SIC/XE 的指令
Von Neumann atchitecture #
- 由 Von Neumann 提出的計算機結構
- 由 Memory, CPU, I/O device 組成
- Memory:儲存指令與資料的地方
- CPU:
- Arithmetic and logic unit:負責運算
- Control unit:負責提取(Fetch)與解碼(Decode)指令
- Memory 與 CPU 間使用 單一匯流排(Single bus) 溝通
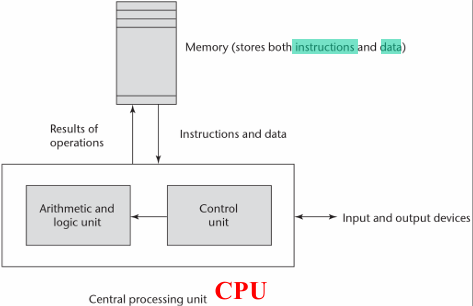
SIC machine Architecture #
Memory #
- 8 bit = 1 bytes, 1 word = 3 bytes
- 總共有 \(2^{15}\) bytes
Registers #
- 每個 register 有 24 bits
- 有五個 register
Mnemonic Number Special use A 0 Accumulator X 1 Index register L 2 Linkage register PC 8 Program counter SW 9 Status word
Data Formats #
在 SIC standard version 中,沒有 floating-point
- Integers:
- 有 24-bit
- 使用 2 補數系統(2’s complement) 表示負數
- Characters:
- 用 8-bit ASCII codes 儲存字元
Instruction Formats #
使用 24 bis 表示

Addressing Modes(定址模式) #
SIC 中有兩種讀取記憶體位址的方式,分別為直接定址(Direct Mode)與索引定址(Indexed Mode)
| Mode | Indication | Target Address Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Direct | X = 0 | TA = address |
| Indexed | X = 1 | TA = address + (X) |
| 其中,X 是 register |
Input/Output #
- 每次傳輸只能傳輸 1 個 bytes
- 用 accumulator (register A) 最右邊 8-bit 進行讀取或寫入
SIC/XE machine Architecture #
Memory #
總共有 \(2^{20}\) bytes
Register #
除了原本五個以外,這邊多了以下四個 register
| Mnemonic | Number | Special use |
|---|---|---|
| B | 3 | Base register |
| S | 4 | General working register |
| T | 5 | General working register |
| F | 6 | Floating-point accumulator (48-bits) |
Data Formats #
除了 SIC 自有的以外,SIC/XE 還多出了 floating-point 的資料型態,共 48-bit

Instruction Formats #
SIC/XE 有四種 instruction format
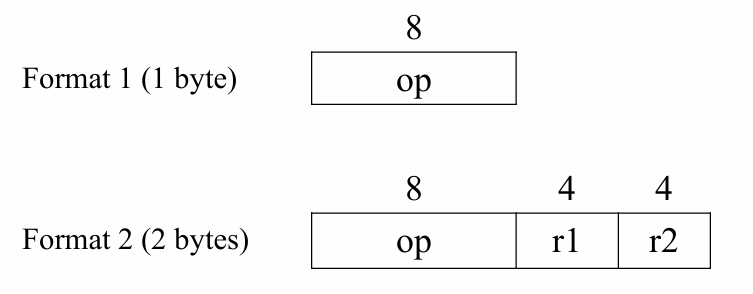
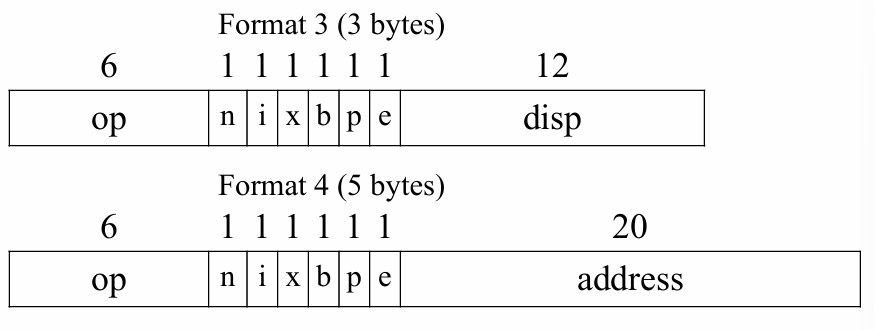
其中 format 3 採用 indexed mode 的方式,其中有以下兩種尋找記憶體位址的方式
| Mode | Indication | Target Address Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Base relative | b = 1, p = 0 | TA = (B) + disp |
| Program-counter relative | b = 0, p = 1 | TA = (PC) + disp |
範例: 當 B = 006000, PC = 003000
指令 A: b = 1, p = 0, disp = 1000 → addr = 6000 + 1000 = 7000
指令 B: b = 0, p = 1, disp = 1000 → addr = 3000 + 1000 = 4000
Input/Output #
- 引入 I/O channels 的概念
- 當 CPU 正在執行其他指令時,還可以用 I/O 通道(I/O channels) 繼續執行輸入和輸出的動作。
